AI Taking Over Jobs: Hype or Reality? How to Prepare? [Infographic]
Table of Contents
It is obvious that artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a faraway concept. Neuralink’s advances in brain-machine interface technology, OpenAI’s GPT-5 launch, and Nvidia’s rising valuation all demonstrate how AI’s influence is growing at an unprecedented rate. It is changing the way we live, work, and play, with particular implications for the labor market.
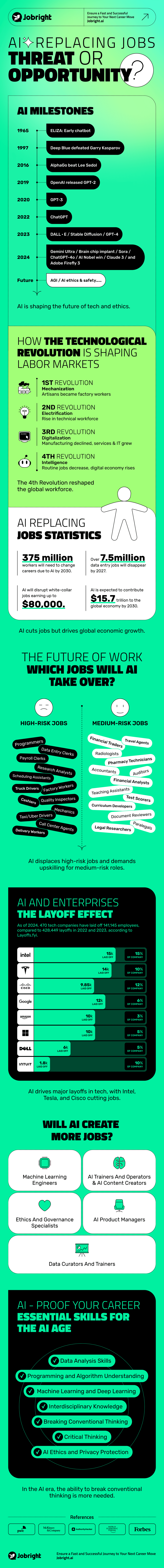
According to McKinsey, by 2030, 14% of the global workforce, or around 375 million workers, will need to change jobs owing to AI. This raises serious concerns: Will AI take your job? What jobs will AI replace, and what will be uniquely human? What skills are required to thrive in the age of AI? And, most crucially, how can we use AI to add value rather than disrupt our careers?
This infographic showcases key facts and figures on AI’s impact on jobs, and how to use AI to your advantage.
Before we get into these topics, let’s look at the history of AI and how previous industrial revolutions changed labor markets. Understanding these tendencies will allow us to better navigate AI’s impact on our careers.
Timeline of AI Development
Here are the major milestones in the evolution of artificial intelligence, from its early beginnings and symbolic AI to significant advances in deep learning and generative AI. This timeline of AI development shows how AI has evolved into a potent tool for affecting the future.
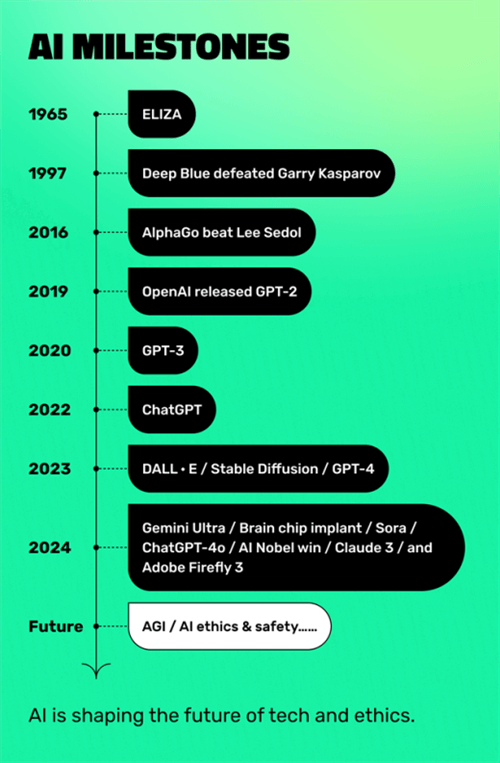
1940s–1970s: Early Foundations
- 1956: “Artificial Intelligence” was coined at the Dartmouth Conference.
- 1965: Joseph Weizenbaum developed ELIZA, an early natural language processing program.
1970s–1980s: “AI Winter”
- AI funding cuts caused the “AI Winter.”
1990s-2010s: Machine Learning Revolution
- 1997: IBM’s Deep Blue defeated chess champion Garry Kasparov.
- 2016: AlphaGo beat champion Lee Sedol
- 2017: Google introduced the Transformer model
- 2019: OpenAI released GPT-2
2020s: Large-Scale AI
- 2020: GPT-3 showcased near-human-level text generation.
- 2022: OpenAI launched ChatGPT.
- 2023: Generative AI: DALL·E, Stable Diffusion, GPT-4
- 2024: Neuralink’s brain-chip implant, OpenAI’s Sora launched, ChatGPT-4o, Claude 3, and Adobe Firefly 3.
Future Trends: AGI, AI ethics & safety……
As you can see, AI is quickly evolving, with noticeable exponential growth in recent years. This shows up in technology advancements and the widespread adoption of AI applications. According to a McKinsey report, AI adoption rates in enterprises have averaged around 50% over the last six years. But by 2024, the percentage had risen to 72%. AI is unstoppable.
The Impact of the Technological Revolution on Labour Markets
In the past, technological disruptions typically affected blue-collar jobs, but now white-collar workers may be feeling the greater impact of these changes.

1st Industrial Revolution (Late 18th – Early 19th Century)
- Technological Breakthroughs: Steam engine, mechanized textiles, railways
- Job Decrease: Artisans (e.g., spinners, weavers)
- Job Increase: Factory workers, railway workers, coal miners
- Structural Change: Shift from agricultural to industrial occupations
2nd Industrial Revolution (Late 19th – Early 20th Century)
- Technological Breakthroughs: Electricity, internal combustion engine, mass production
- Job Decrease: Some traditional manufacturing roles
- Job Increase: Power system operators, electrical repairs, automobile workers, oil workers
- Structural Change: Growth in manufacturing, rising demand for technical and managerial talent
3rd Industrial Revolution (Mid-20th Century – 1980s)
- Technological Breakthroughs: Automation, electronics, computers, telecommunications
- Job Decrease: Blue-collar manufacturing jobs, mid-skill roles
- Job Increase: White-collar service jobs, IT roles (e.g., software developers, computer scientists)
- Structural Change: Polarization of skills, labor market divides, rise in service jobs, globalization and outsourcing reduced local demand
4th Industrial Revolution (21st Century – Present)
- Technological Breakthroughs: AI, robotics, IoT, advanced automation, biotechnology
- Job Decrease: Routine manual and cognitive tasks (e.g., data entry, assembly line jobs, cashiers)
- Job Increase: Digital skills jobs (e.g., AI, machine learning, data science, cloud computing), gig economy freelancers
- Structural change: Job polarization, automation replacing mid-skill jobs, growing skill gap, rising income inequality, and increased need for reskilling.
Technological advancements may reduce employment in the short term but could increase it in the long term. The first three industrial revolutions all contributed to increased job demand. For instance, during the Second Industrial Revolution, the U.S. manufacturing workforce grew from about 7 million in 1880 to over 15 million by 1920 (PMC). In the third industrial revolution, the U.S. economy shifted from manufacturing to services, with around 70% of the workforce employed in services by the late 1990s (CIAO).
While history can be viewed objectively, people’s reactions to change are diverse—some are excited, while others fear or resist it. Let us use the limited data available today to glimpse into the future.
Top AI Replacing Jobs Statistics
Let’s look at some AI job replacement statistics to understand how artificial intelligence currently impacts the global job market.
Editor’s Picks:
- By 2027, over 7.5 million data entry jobs will disappear (WEF).
- Compared to the historical impact on blue-collar workers, the job disruption caused by AI is now primarily targeting educated white-collar workers with annual incomes up to $80,000. This is mainly due to the automation of roles involving programming and writing skills, with technologies like ChatGPT being a prime example of this shift (Business Insider).
- 42% of employers will prioritize training employees in AI skills by 2027(WEF).
- By 2025, AI is expected to eliminate 85 million jobs while creating 97 million new ones, resulting in a net increase of 12 million jobs(WEF).
- AI is expected to contribute $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2023(PwC).
- In the next decade, 47% of American workers risk losing their jobs due to automation (CEPR).
What Jobs Will AI Replace?
Based on the data above, the impact of AI on the job market is more significant than we imagined. So, which jobs will AI replace, and why are these jobs more susceptible? Will AI replace programmers? Will AI replace lawyers? You can find the answers in this section.

High-Risk Jobs
These jobs are mostly repetitive, and predictable, or involve routine tasks that AI and robots can perform more efficiently.
Entry-level programming jobs
Since programming uses structured language, tools like ChatGPT can help write code. AI can generate code automatically, suggest code blocks, and spot errors. It can also handle repetitive tasks by learning patterns across projects and quickly replicating similar code.
Data Entry Clerks, Payroll Clerks, and Scheduling Assistants
These roles rely on structured, repetitive workflows that AI algorithms can handle efficiently. For example, AI tools like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) automate data entry, and virtual assistants (e.g., chatbots, scheduling apps) manage calendars and emails.
Factory Workers, Mechanics, and Quality Inspectors
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and industrial robots can perform repetitive physical tasks with higher precision and fewer errors. For example, robots like Fanuc and KUKA work in the automotive and electronics industries. Fully automated smart factories (e.g., Tesla’s Gigafactory) are becoming more common, and AI vision systems replace human quality inspectors.
Truck Drivers, Delivery Workers, and Taxi/Uber Drivers
Advances in autonomous driving technology threaten to replace human drivers. AI systems powered by computer vision and lidar sensors can navigate roads autonomously. Companies like Waymo, Tesla, and Aurora are developing self-driving cars and trucks. At the same time, drones and robots are being tested for last-mile delivery (e.g., Amazon Prime Air, and Starship Technologies).
Cashiers, Sales Assistants, and Call Center Agents
AI systems can handle transactions and customer interactions without human intervention. For instance, self-checkout machines are replacing cashiers in grocery stores, and AI chatbots like Zendesk and Intercom manage customer inquiries, complaints, and tech support.
Medium Risk Jobs
These roles involve repetitive tasks (AI can automate) and complex tasks that still require human oversight. AI may enhance, but not completely replace, these jobs.
Radiologists and Pharmacy Technicians
AI can analyze medical data with incredible speed and accuracy, especially in pattern-based tasks like diagnosis and imaging. Tools like Google DeepMind and IBM Watson Health help diagnose diseases like cancer using imaging data. Pharmacy automation (e.g., robotic pill dispensers) reduces the need for pharmacy technicians.
Accountants, Auditors, and Financial Analysts
AI excels at analyzing large datasets, identifying patterns, and making predictions—key tasks in finance. Apps like Xero and QuickBooks automate bookkeeping and tax preparation, while AI fraud detection systems like FICO Falcon spot suspicious transactions.
Test Scorers, Teaching Assistants, and Curriculum Developers
AI tools can automate grading, create personalized lesson plans, and even tutor students. AI-driven platforms like Khan Academy offer adaptive learning experiences, and AI scoring systems for essays and exams are becoming more common. However, human teachers are still needed for tasks requiring emotional intelligence and creativity, such as classroom management and motivating students.
Paralegals, Legal Researchers, and Document Reviewers
AI can quickly scan and analyze legal documents, reducing the need for human researchers. Tools like Kira Systems and ROSS Intelligence assist with contract analysis and legal research, while e-discovery software automates document searches in litigation. However, lawyers will still play a key role in courtroom representation and crafting legal arguments.
AI Technology Impact on Enterprises
If you think the previous content sounds like hype or just marketing, the data I’m about to share might change your perspective.
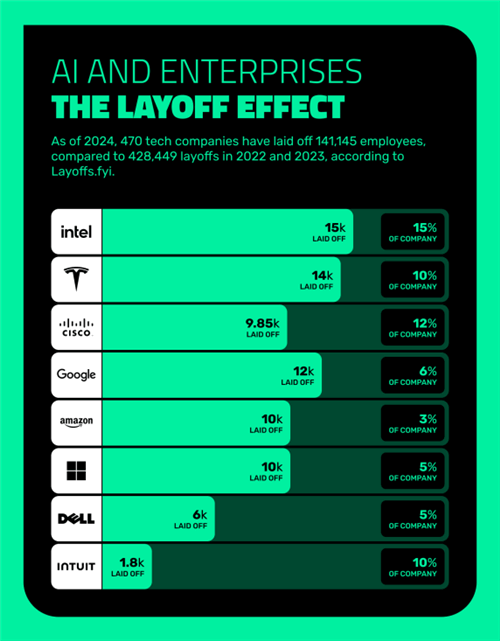
According to data from Layoffs.fyi, as of October 2024, 470 tech companies worldwide laid off approximately 141,145 employees in 2024, while 428,449 tech workers were laid off in 2022 and 2023.
- Dell laid off 5% of its workforce in March, nearly 6,000 people. source
- In July, Intuit announced plans to lay off 1,800 employees and shift its focus to hiring AI talent while reducing its executive staff by 10%.
- In August, Intel announced it would reduce its global workforce by 15%, cutting about 15,000 jobs. source
- Cisco Systems announced plans to lay off 7% of its workforce due to a shift in priorities toward AI and cybersecurity, after laying off over 4,000 employees in February. source
- Integrating the generative AI development assistant “Amazon Q” into its internal systems saved the equivalent of about 4,500 developers’ work for one year and saved $260 million in operational costs.
The adoption of AI is changing organizational priorities, leading to workforce cutbacks in traditional roles and higher demand for AI skills. Intuit and Cisco are reallocating resources to AI and cybersecurity, indicating a strategic change. While these changes cause short-term disruptions, they reflect a long-term trend toward increased efficiency and scalability with a smaller human workforce.
Jobs That AI Can’t Replace
Even as artificial intelligence technology continues to advance and human-machine integration deepens, certain jobs remain irreplaceable by AI, as these roles demand profound empathy, emotional depth, critical thinking, human creativity, and a certain level of interpersonal interaction – qualities that AI cannot replicate. Let’s take a closer look at the kinds of jobs AI can’t replace:
Creative Roles
- Examples: Writers, artists, designers, filmmakers.
- Why they resist: While AI can generate content (e.g., DALL·E for art, ChatGPT for writing), human creativity and originality remain crucial for producing high-quality, impactful work. AI can assist with creative or repetitive tasks but rarely fully replaces humans.
- Trend: AI tools like Canva and Adobe Sensei enhance rather than replace human creativity. Creative professionals increasingly collaborate with AI to push boundaries.
Skilled Trades
- Examples: Electricians, plumbers, mechanics.
- Why they resist: These jobs require physical dexterity, adaptability, and the ability to solve problems in unpredictable environments.
- Trend: Some automation tools, like robotic assistants, may enhance skilled trades but won’t fully replace them.
Interpersonal and Leadership Roles
- Examples: HR professionals, therapists, social workers, teachers, and managers.
- Why they resist: These roles involve emotional intelligence, empathy, and interpersonal communication – qualities AI cannot replicate. Leadership requires strategic thinking, ethical decisions, and human connections.
- Trend: AI may provide decision support or tools for administrative tasks, but the human element remains essential.
Jobs Created by AI
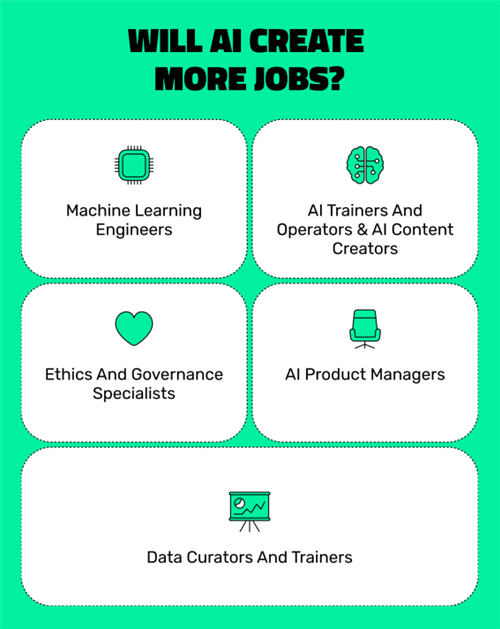
In fact, as AI applications continue to grow, it’s not just replacing jobs – it’s also creating new opportunities. This expansion not only calls for professionals with new skill sets to manage AI but also boosts the demand for millions of skilled workers to take on creative roles. Here are some of the emerging roles powered by artificial intelligence.
- Machine Learning Engineers: Focus on designing, developing, and optimizing machine learning models and algorithms.
- Data Curators and Trainers: Responsible for collecting, cleaning, labeling, and organizing data to provide high-quality training datasets for AI models.
- AI Trainers and Operators: Train and operate AI systems to ensure they perform as required.
- AI Content Creators: Use AI technologies to generate content such as text, images, or videos.
- AI Product Managers: Plan and manage the development and implementation of AI products, ensuring they meet user needs and market goals.
- Ethics and Governance Specialists: Ensure AI technologies comply with ethical standards and governance frameworks, assessing and mitigating potential risks.
How to Prepare Yourself for the Age of AI
In the age of AI, the focus shifts from what humans can do to what they can achieve. While AI transforms industries, uniquely human skills like communication, critical thinking, and empathy remain essential.
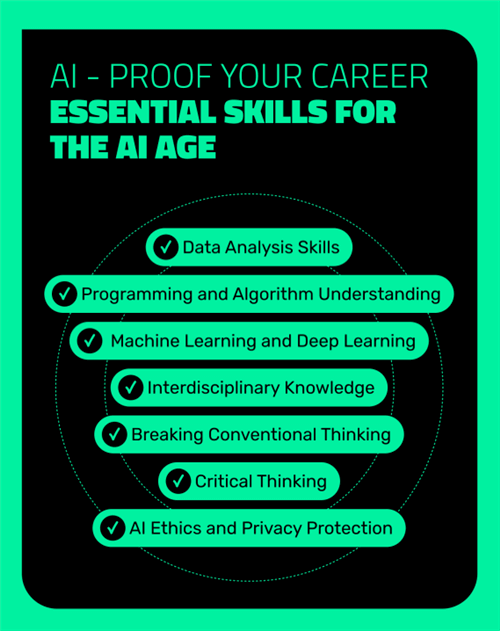
Here are some skills you must have in the age of AI:
1. Data Analysis Skills
The ability to process and analyze large datasets, using tools like SQL, Python, or R for data preprocessing and exploratory data analysis. Mastery of statistics and data visualization techniques is essential for extracting valuable insights from data.
2. Programming and Algorithm Understanding
Proficiency in at least one programming language (such as Python or Java) and a solid understanding of basic algorithms and data structures. This helps in interacting with AI systems and developing AI applications.
3. Knowledge of Machine Learning and Deep Learning
A grasp of the fundamentals of machine learning principles and algorithms and the ability to use frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch for model training and optimization.
4. Interdisciplinary Knowledge
A strong foundation in computer science, mathematics, and statistics to better understand the principles and applications of AI technologies.
5. Innovation (Breaking Conventional Thinking)
In the age of AI, innovative thinking is crucial. The ability to propose new solutions and applications is a valuable skill.
6. Critical Thinking
Effectively leveraging AI requires experience and critical thinking skills to understand the insights provided by models within a broader industry context.
7. AI Ethics and Privacy Protection
An understanding of AI ethical principles and privacy protection techniques to ensure adherence to moral standards when developing and applying AI technologies.
These soft skills enable collaboration and innovation – areas where humans excel.
Infographic for AI Taking Over Jobs
Check the full infographic, and feel free to share it on social media, or embed it on your site!
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence complements humanity rather than replacing it. Instead of fearing that artificial intelligence will take over our jobs, we ought to use it to improve our efficiency and talents at work.
In navigating the AI era, adopting a proactive and optimistic mindset is essential. By continuously refining our skills and adapting to the transformations and uncertainties brought about by technological advancements, we can unlock new opportunities. Dwelling on the dread of being replaced achieves little; instead, we should focus on using AI to maximize our potential and enhance our distinctive contributions.
